In the year 2005, when VAT was to be implemented, i made this write up... still most of it would be useful...
History of VAT
·VAT was first introduced in France in 1954.
·It was primarily aimed at simplification of commodity taxes
·More than 130 countries in the world have adopted VAT system
·Out of the bigger countries, except India and USA almost all the nations have adopted VAT
·All over the world VAT is levied on both goods and services
·Compliance system in VAT Nations is very simple with minimum interface between taxpayer and the tax collector. However, non compliance involves very high penalty
VAT in India
·When reforms started in 1991, National Institute of Public Finance & Policy (NIPFP) studied the indirect structure and recommended VAT system to replace CST / LST system
·In 1994, Empowered Committee of All States’ Finance Ministers constituted for successful launch VAT System in India
·The Empowered Committee has accomplished the following :
a)Abolition of incentive schemes in sales tax effective 01/01/2000
b)Uniform rates of tax for almost all major commodities
c)Compensation towards loss of revenue to the states
d)Implementation of VAT by the states from 01/04/2005
e)Phasing out plan for CST
Proposed Tax System
By the Central Government
·Excise Duty – Cenvat System
·Service Tax – Cenvat System
Through Indian Goods & Services Tax Act (Central – GST) (Dr.Kelkar committee report)
By the State Governments
·VAT to replace present state taxes like sales tax, works contract tax, lease tax, turnover tax etc. However, levies like Octroi not within the jurisdiction of Central or State Governments would not be replaced by VAT immediately
Through State Goods and Services Tax Act (State GST) (Merger of all state taxes and service tax levy by the state
Note : On the same goods or services the Central Government would levy Central GST and States would levy State GST
Constitution and Sales Tax
·The Constitution of India empowers State / Central Governments to levy, collect and retain sales tax and sales tax is the largest source of revenue for States.
·Sales Tax is a tax on sale of movable goods, i.e., the transaction should involve, sale (transfer of title), goods, which are movable.
·Movement of goods decides the tax collectors entitlement
·The Central Sales Tax is collected by State of despatch and also retained by it and the administration of CST is delegated to the States
·Imports, Exports and Sales in the course of imports / exports are exempted from sales tax
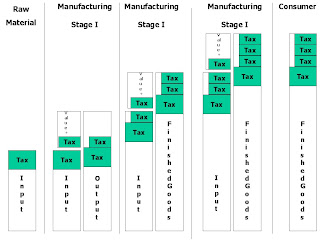
How the VAT system works
·VAT is a system of taxation of local sales tax
·It is a multipoint tax system with set off available for tax paid on corresponding purchases
·Full tax is collected at each transaction but paid on the value added portions only. Hence it is called value added tax.
·Since the input tax burden is nullified, there is no cascading effect in the supply chain.
·The tax is ultimately levied on the final consumption and is fully borne by the final consumer
Design of VAT (To be implemented from 01/04/2005)
·No resale concept, i.e., all the sales is taxable and fully taxable.
·All local declaration forms which allow concessional rates or tax free purchase withdrawn
·Uniform tax rates across states on the commodities
o Essential Commodities – Nil
States empowered to have flexibility in deciding exemption for some items
o Raw Material and Industrial Inputs – 4%
This will include medicines, capital goods, IT Goods etc
o Residuary rate – 12.5%
This covers those items which have not been specified in the above two categories
·Gold and silver articles would carry 1% and Liquor etc would carry 20% as per the existing tax structure. Also for HSD, Petrol, ATF the current tax structure would continue in 05-06
·If any State decide to levy entry tax, that will also be Vatable
·4% tax (Current CST Equivalent) retention by the State Government on Local Inputs when the corresponding Finished Goods are transferred to Outside the State. This is to ensure smooth transition from CST regime (where the State Government enjoys retention of tax on Interstate Sale) to VAT regime. By this process full input tax credit would not be allowed to manufacturers on interstate sales / transfers till CST rate becomes Nil)
·Carry forward of VAT balance is allowed for a period between 24 months to 36 months as the States may deem fit.
Incentives Schemes under VAT Regime
·No exemption scheme would continue. States to decide on conversion of exemption scheme to deferral scheme
·Considering the Interest of the Incentive Units, States to redesign the Incentive schemes so that no VAT design is disturbed
·There is a composition scheme which allows Traders / Retailers having annual turnover of less than 50 Lakhs to pay a composite tax of 1% of the turnover and stay out of VAT chain. These traders are not allowed to issue VAT invoice
Tax Invoice
·VAT / CST Registration (Tax Identification No – TIN)
·Any declaration, if prescribed, under the Local VAT Act
·Local sales tax (VAT) should be separately charged
·Input tax credit would be allowed only on the basis of the Tax invoice from the seller
Comparison of Current Sales Tax and Proposed VAT Systems
Present – State Sales Tax Design
Proposed VAT Design
Single Point System of Tax – No Tax on resale
Multipoint system of Tax with set off available on corresponding purchase. No resales.
Forms for concessional tax rates
No local declaration forms or concessions
Many tax rates – TOT, SC, Resale tax, Cess etc.,
Only 3 basic rates
No composition scheme
Optional composition scheme for small traders
Separate Acts for different types of taxes, viz., Works Contracts, Lease, Entry etc.,
All are covered under one State VAT Act
No defined invoice controlling tax flow
Mandatory tax invoice
Concession Forms for Input purchases to manufacturers – Net Burden 3 – 5 %
Full input tax credit available – Net Burden 0 – 4 %
No sales tax on AED Products viz., textiles, sugar, tobacco etc
AED Products not covered under VAT system
Annual Assessments
Periodical Sampled Compliance Audit
Important Areas – Vague issues under VAT System
·Discounts
·Sales Returns
·Free Samples / Gifts
·Unregistered Dealer Purchases
·Closing stock as on 31/03/2005
·Set Off on Capital Purchases and Capital Goods definition
·Overlap of VAT and Service tax in
o Job works / Labour Jobs
o Outsourced Jobs
o AMCs, Erecition & Commissioning, Authorised Service Stations
Documentation / Records under VAT
·Tax Invoice
·Purchase Register
·Sales Register
·Identification Register for Traders
·VAT Registration Certificate
Any State Specific record prescribed, if any.
Proper Tax Planning
·Till phasing out of CST
o Interstate purchases would not be vattable and hence will have negative impact
o Stock transfer would not be eligible for input VAT and hence will have negative impact
o The best scenario would be to have 100% Inputs locally purchased and 100% of sales from the manufacturing location
·Post CST Phase out
o All the negative impact listed above would stand rectified
o Undisturbed flow of VAT across the value chain would get established and would work in line with the current Excise Cenvat System
Conclusion
·In spite of all the guidelines and procedures, if VAT embraces industry specific anomalies similar to those in the current Excise Structure, abnormalities in those industries would persist.
·With implementation pending in some states, Industries are not properly placed to adopt the benefits of VAT structure yet.Without phasing out the CST effect, VAT would not be available to the industries in its entirety.
